Mobile Phone Biometrics: Features, Benefits & Security
Published: 12 Feb 2026
Mobile phone biometrics means using your body features to unlock and protect your phone. It includes fingerprint, face, iris, voice, and behavior recognition. You already use mobile phone biometrics when you unlock your phone, log in to banking apps, or approve payments. This technology makes access fast and secure because you do not need to remember passwords or PIN codes. Your fingerprint or face becomes your identity, which is hard for others to copy. That is why mobile phone biometrics is now an important part of daily smartphone security.
How Mobile Phone Biometrics Work
Mobile phone biometrics works in simple steps. The phone first learns your biometric data, then stores it safely, and finally checks it each time you unlock your device.
Enrollment & Matching
During enrollment, your phone scans your fingerprint or face and creates a digital pattern. Later, it compares new scans with the saved pattern to confirm your identity.
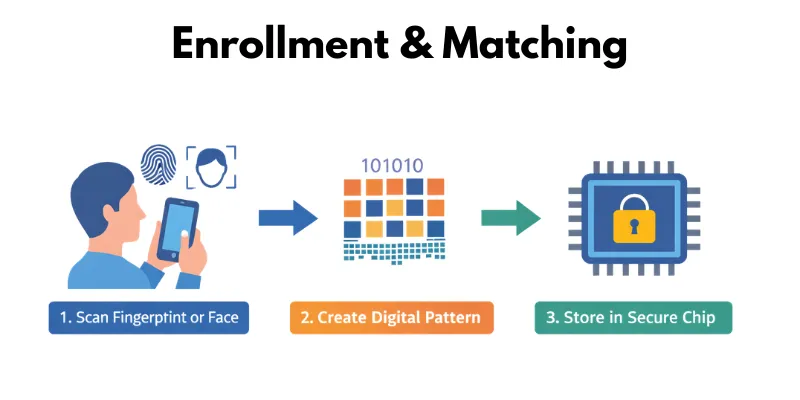
- The phone scans your fingerprint or face during setup.
- It creates a unique digital pattern from the scan.
- Each time you unlock, the phone matches the new scan with the saved pattern.
Biometric Template Storage & Security
Your phone does not store real images of your fingerprint or face. Instead, it saves a small coded template of just a few MB inside a secure part of the device to protect your data.
- The phone converts your biometric scan into a coded template.
- The template stays inside a secure chip in the device.
- Apps and hackers cannot easily access this stored template.
Liveness Detection & Anti-Spoofing
Phones check whether the biometric input is real and live. This step prevents people from using fake photos or copied fingerprints.
- Face unlock checks blinking, movement, or depth of the face.
- Fingerprint sensors check skin texture and natural signals.
- These checks stop fake photos, masks, or copied fingerprints from unlocking the phone.
Main Types of Mobile Biometrics
Mobile phones use different biometric methods to identify users. Each method has its own strengths, limits, and real-life uses.
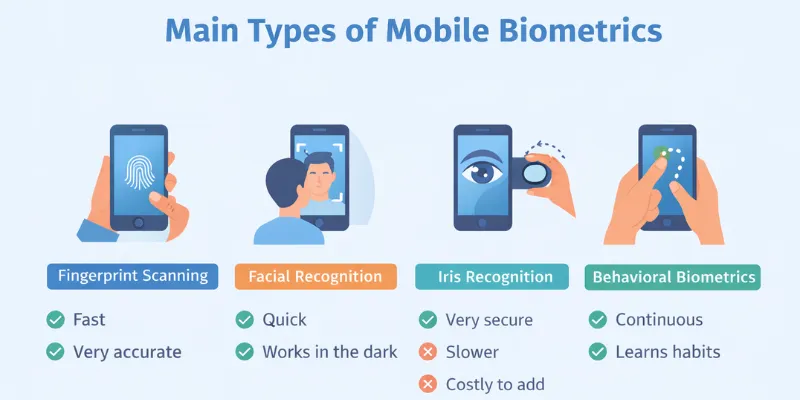
Fingerprint Scanning
Fingerprint scanning is the most common mobile phone biometrics method. Users simply touch a sensor to unlock the device or approve payments.
- Uses optical, capacitive, or ultrasonic sensors in phones.
- Works fast and accurately in daily use.
- May fail if fingers are wet, dirty, or injured.
Facial Recognition
Facial recognition unlocks the phone by scanning the user’s face. Some phones use advanced 3D or infrared systems for better accuracy.
- 2D face unlock uses the front camera and works less securely.
- Infrared or 3D scanning works better in low light.
- Bright sunlight, masks, or extreme angles can affect accuracy.
Iris & Retina Recognition
Iris and retina recognition scan the unique patterns in the eyes. Few smartphones use this method because the setup is costly and slower for daily use.
- Provides very high security compared to other methods.
- Requires users to hold the phone close to their eyes.
- Limited adoption due to cost and user convenience issues.
Behavioral Biometrics (Emerging)
Behavioral biometrics studies how a person interacts with the phone. It checks typing style, touch patterns, or walking movement to verify identity.
- Monitors typing speed, swipe style, and touch pressure.
- Works in the background for continuous authentication.
- Useful for banking and security apps to detect unusual behavior.
Where Biometric Authentication Is Used
Mobile phone biometrics is not just for unlocking your device. Many industries now use biometric authentication to improve security and user experience. Let’s look at real-world examples.
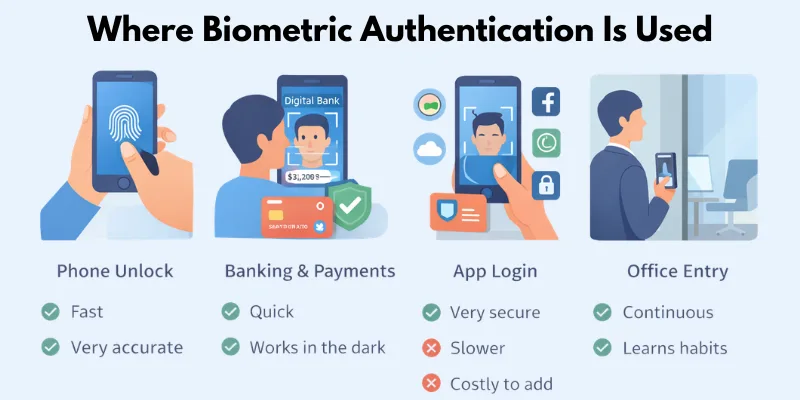
Device Unlock
Most people use biometrics to unlock their phones every day.
- Users unlock phones with a fingerprint or a face scan in seconds.
- No need to remember long passwords or PIN codes.
- Quick access improves daily convenience and security.
Example: You pick up your phone, look at it, and it unlocks instantly. Simple and fast.
Mobile Banking & eKYC
Banks use mobile phone biometrics to protect accounts and verify identity.
- Users log in to banking apps using fingerprint or face scan.
- Banks verify customers during account opening through eKYC.
- Biometric checks reduce fraud and identity theft.
Example: When you open a digital bank account, the app scans your face and matches it with your ID card. This process confirms your identity safely.
App-Level Authentication
Many apps add extra biometric protection to the phone.
- Payment apps require a fingerprint for transaction approval.
- Social media apps protect private chats with face lock.
- Cloud storage apps use biometric login for data safety.
Example: You approve an online payment by touching the fingerprint sensor instead of typing a password.
Government & Enterprise Identity
Governments and companies also use biometric systems for secure access.
- Governments use biometrics for digital ID programs.
- Offices use fingerprint or face access for employees.
- Enterprises protect sensitive data with biometric login.
Example: An employee enters the office using a face scan instead of an ID card. The system records attendance automatically.
Advantages & Disadvantages of Mobile Phone Biometrics
Mobile phone biometrics make unlocking devices and accessing apps fast, easy, and secure. They reduce reliance on passwords and lower the risk of theft or fraud. However, they also have limitations like privacy concerns, spoofing attacks, and accessibility challenges. Knowing both sides helps you use this technology safely.
Advantages of Mobile Phone Biometrics
- Fast and convenient – Unlock phones or approve payments in seconds without typing passwords.
- Harder to steal – Fingerprints, faces, or iris patterns are difficult for hackers to copy.
- Better than passwords/2FA – Unlike passwords or SMS codes, biometrics cannot be guessed or intercepted easily.
- Legal and compliance benefits – Some banking and enterprise systems accept biometrics for identity verification.
- Enhanced user experience – Smooth and seamless authentication improves everyday mobile use.
Disadvantages / Risks of Mobile Phone Biometrics
- Privacy and consent issues – Biometric data is personal, and misuse can raise legal or ethical concerns.
- Spoofing & attacks – Hackers may try fake fingerprints, photos, or template theft to bypass security.
- False accept/reject errors – Sensors may occasionally fail, either allowing unauthorized access or denying the owner.
- Accessibility & inclusivity concerns – Some users (e.g., injuries, disabilities) may struggle to use certain biometrics.
- Single point of failure – If the biometric system is compromised, it can be harder to recover access than with a password.
Best Practices for Secure Implementation
Using mobile phone biometrics is safe when combined with smart security practices. Following these steps helps protect your data and reduces risks from spoofing or system failures.
Key Best Practices
- Always use a backup PIN or password – If the biometric system fails, you can still unlock your device.
- Keep software updated – Regular updates fix security flaws in sensors and authentication systems.
- Combine with MFA or passkeys – Adding multi-factor authentication strengthens protection for apps and accounts.
- Secure storage of biometric templates – Use Trusted Execution Environment (TEE), Secure Element (SE), or tokenization to keep templates safe.
- Monitor unusual activity – Watch for failed unlock attempts or suspicious behavior on your device.
Following these practices ensures that mobile phone biometrics stay fast, convenient, and secure, giving you peace of mind in everyday use.
Future Trends in Mobile Phone Biometrics
mobile phone biometrics is evolving fast. New technologies aim to make authentication smarter, safer, and more convenient.
Key Future Trends
- Multimodal biometrics – Combining fingerprint, face, iris, or voice for layered security and higher accuracy.
- AI-driven behavioral profiling – Using machine learning to monitor patterns like typing, swiping, or walking for continuous authentication.
- Tokenization of biometric data – Storing only encrypted tokens instead of raw biometric templates to reduce risk if data is stolen.
These innovations show that mobile phone biometrics will not only stay relevant but also become more secure, intelligent, and seamless in the years ahead.
Conclusion
So guys, in this article, we’ve covered mobile phone biometrics in detail. From fingerprints and face scans to iris recognition and behavioral authentication, these tools make your devices faster, safer, and more convenient. Personally, I recommend using biometrics along with a backup PIN and keeping your software updated for the best security. Start exploring your phone’s biometric features today and enjoy quick, secure access like never before.
FAQs
Biometrics are very secure, but not 100% foolproof. Hackers could try fake fingerprints, photos, or template attacks. Using backups and keeping software updated makes it safer.
Yes. Mobile phone biometrics are harder to guess or steal than passwords or PIN codes, making them more reliable for everyday use.
Biometric templates are stored securely, not as real images. If compromised, systems can revoke the template and let you re-enroll your data.
Yes. The same fingerprint or face scan can unlock your phone and verify identity in banking, payment, or social media apps.
Some sensors may fail with wet fingers, cuts, or masks. Backup PINs or passwords are important for these situations.
No. Some phones use fingerprints, others face recognition, iris scans, or behavioral biometrics. Features depend on the device and brand.
Not always. Biometric authentication is fast and secure, but combining it with PINs, passwords, or multi-factor authentication gives the best protection.

- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks

- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks